Student Learning Outcomes
Student Learning Outcomes (SLOs) are specific, measurable, and observable statements that describe what students should know or be able to do after completing a course, program, or activity. Effective SLOs provide clear and measurable goals for students, help teachers focus instruction, and ensure that assessments align with learning goals. They describe what students will be able to do as the result of a learning experience. These include the knowledge, skills, attitudes, and habits of mind that students take with them from a learning experience. SLOs should include the most important concepts, ideas, methods, theories, approaches, and perspectives that your students should learn in your course and/or program.
Learn more about the assessment process »
Effective Learning Outcomes
Below are some characteristics of effective student learning outcomes:
- Learning outcomes should be specific and well defined.
- Learning outcomes should be realistic, rigorous, and achievable.
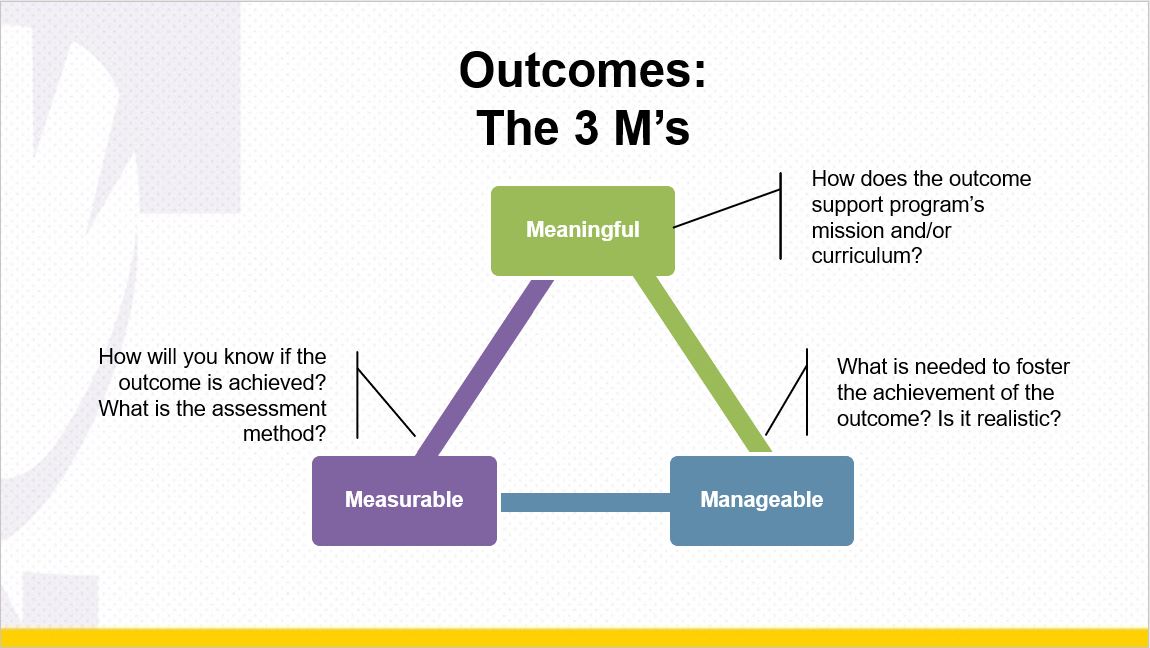
- Learning outcomes should be meaningful.
- Learning outcomes should be measurable.
- Learning outcomes should be manageable.
- Learning outcomes should be written in simple language with active verbs.
- Learning outcomes should align with the program's curriculum.
Components of SLOs
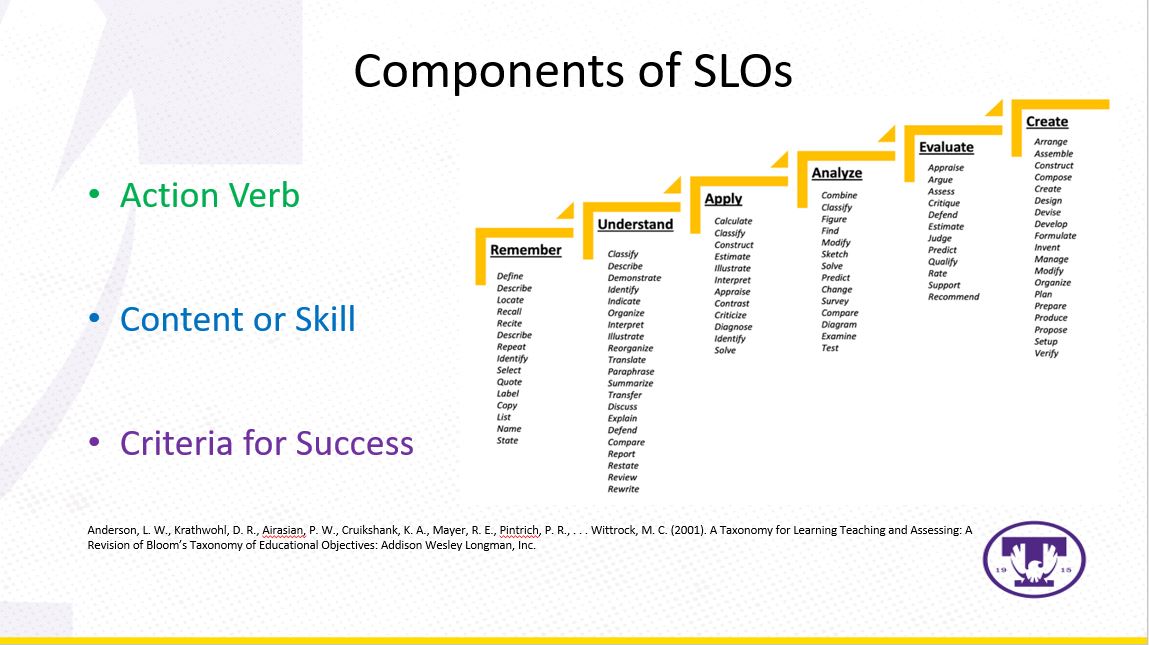
Action Verbs
Action verbs are critical components of SLOs because they describe the observable behavior or action that the student will demonstrate. Effective action verbs are specific, measurable, and generally focus on higher-order thinking skills. Taxonomies of educational objectives can be used as a guide for developing SLOs. The most well known educational objective taxonomy is Bloom’s Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (1956). Levels of performance in this taxonomy include knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation. There are also other popular taxonomies which include Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy (2001), the Taxonomy of Significant Learning (Fink, 2013), Dimensions of Learning (Marzano, Pickering, & McTighe, 1993), and Taxonomy of Educational Objectives (Marzano & Kendall, 2008).
Content or Skill
The second component (content or skill) describes what the student will learn or be able to do. Effective SLOs should focus on important content or skills that are aligned with the learning goals of the course, program, or activity.
Criteria for Success
The final component is the criteria for success. Criteria for success describes how the student will be assessed or evaluated. Effective criteria for success are specific, measurable, and aligned with the content or skill being assessed. Examples of effective criteria include accuracy, completeness, creativity, and meeting established standards or expectations. These criteria might include performance on tests or exams, completion of assignments or projects, or other forms of assessment.
SLO Examples
- Students will be able to identify and explain the key elements of a persuasive argument.
- Students will be able to analyze and interpret statistical data using appropriate measures of central tendency and variability.
- Students will be able to create and maintain a safe and inclusive classroom environment that promotes learning and student engagement.
- Students will be able to design effective instructional activities and assessments that align with learning objectives and engage students in meaningful learning.
Tips for Writing Effective SLOs
- Start with clear goals
- Use specific and measurable language
- Use action verbs
- Focus on what matters
- Be realistic
- Consider the audience
- Align with assessments
- Review and revise
Online Resources
- Boston University – Creating Learning Outcomes
- Georgia Tech – Developing Student Learning Outcome Statements
- Stanford – Creating Learning Outcomes
- IUPUI – Writing and Assessing Student Learning Outcomes
- University of Wisconsin-Madison – Writing Student Learning Outcomes
- Easy Generator – Learning Objective Generator